The realm of laser cutting, a marvel blending precision and versatility, has revolutionized how we shape the world around us. From the delicate intricacies of jewelry to the robust components of aerospace engineering, laser cutting technology is an indispensable tool across various industries. This article delves into the multifaceted applications of laser cutting, showcasing its pivotal role in shaping modern industry.
What Is Laser Cutting?
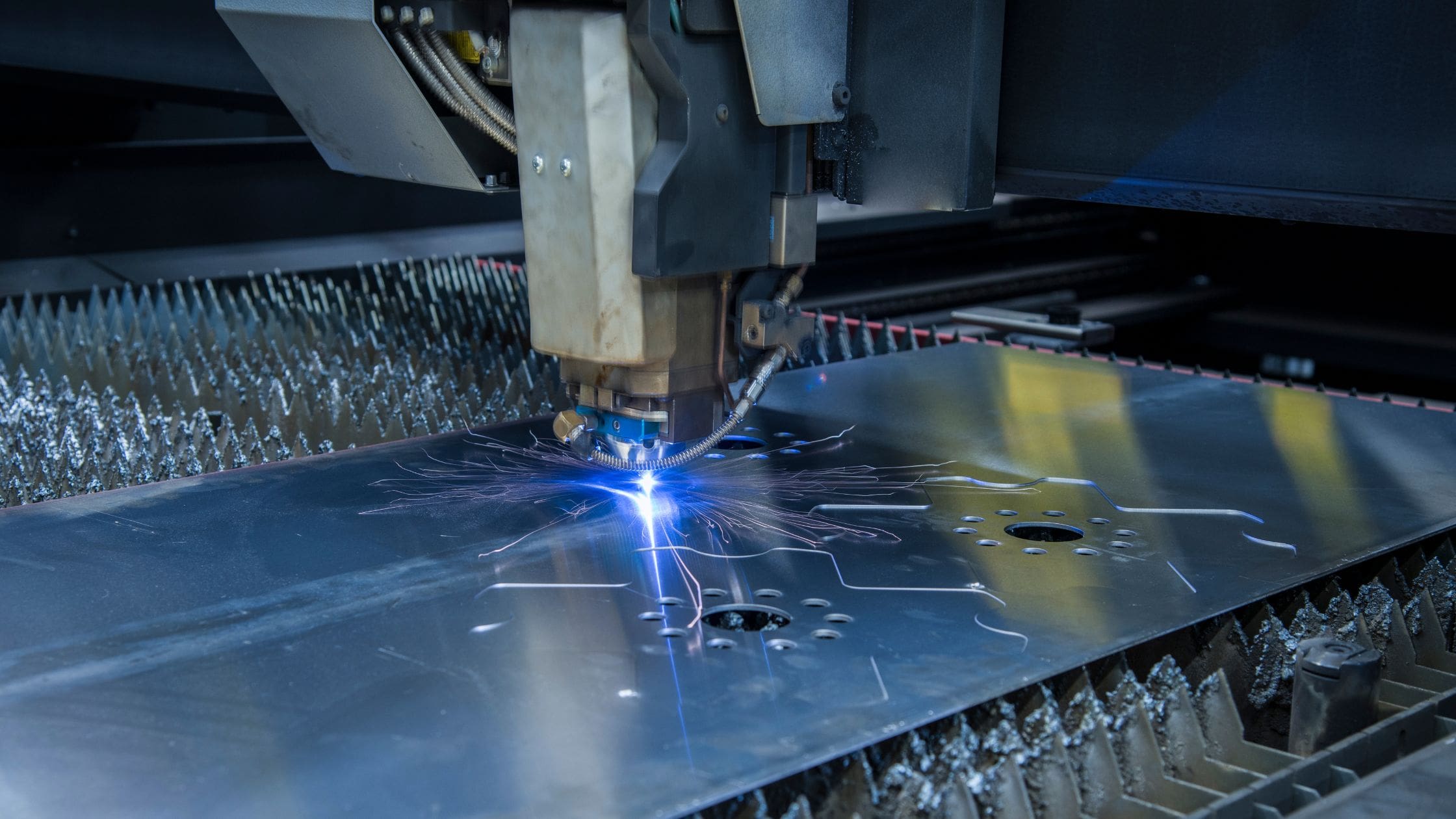

Laser cutting, a process involving the use of a high-power laser beam, has transformed manufacturing and fabrication. This technology, evolving since its inception, employs a focused laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize material, offering unparalleled precision. Originating from the concept of computer numerical control (CNC), laser cutting stands as a testament to the synergy between innovation and practicality.
What Are The Applications of Laser Cutting Technology in Various Industries?
The versatility of laser cutting technology, a marvel in the manufacturing and fabrication world, is unparalleled. As a cornerstone of modern industry, it has opened new horizons in production, creativity, and precision.
This technology, utilizing a concentrated laser beam—be it CO2, fiber, or solid-state lasers—has revolutionized how materials are cut and shaped.
Let’s explore how laser cutting is applied across various industries, emphasizing its adaptability and the intricacies of its usage.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, laser cutting stands as a pivotal tool, especially for crafting intricate components and customizations.
This process, driven by high precision and efficiency, allows manufacturers to produce parts that are both complex and delicate, using a variety of materials from stainless steel to aluminum alloys.
- Examples of automotive parts made via laser cutting:
- Precision-cut body panels for aesthetic and aerodynamic enhancements.
- Engine components shaped with extreme accuracy.
The laser cutting method, significantly more efficient than traditional metal fabrication processes like die cutting or plasma cutting, has streamlined vehicle manufacturing. The high power laser, typically a fiber laser cutter, provides a level of precision that is essential in the automotive field where every millimeter counts.
Aerospace Industry
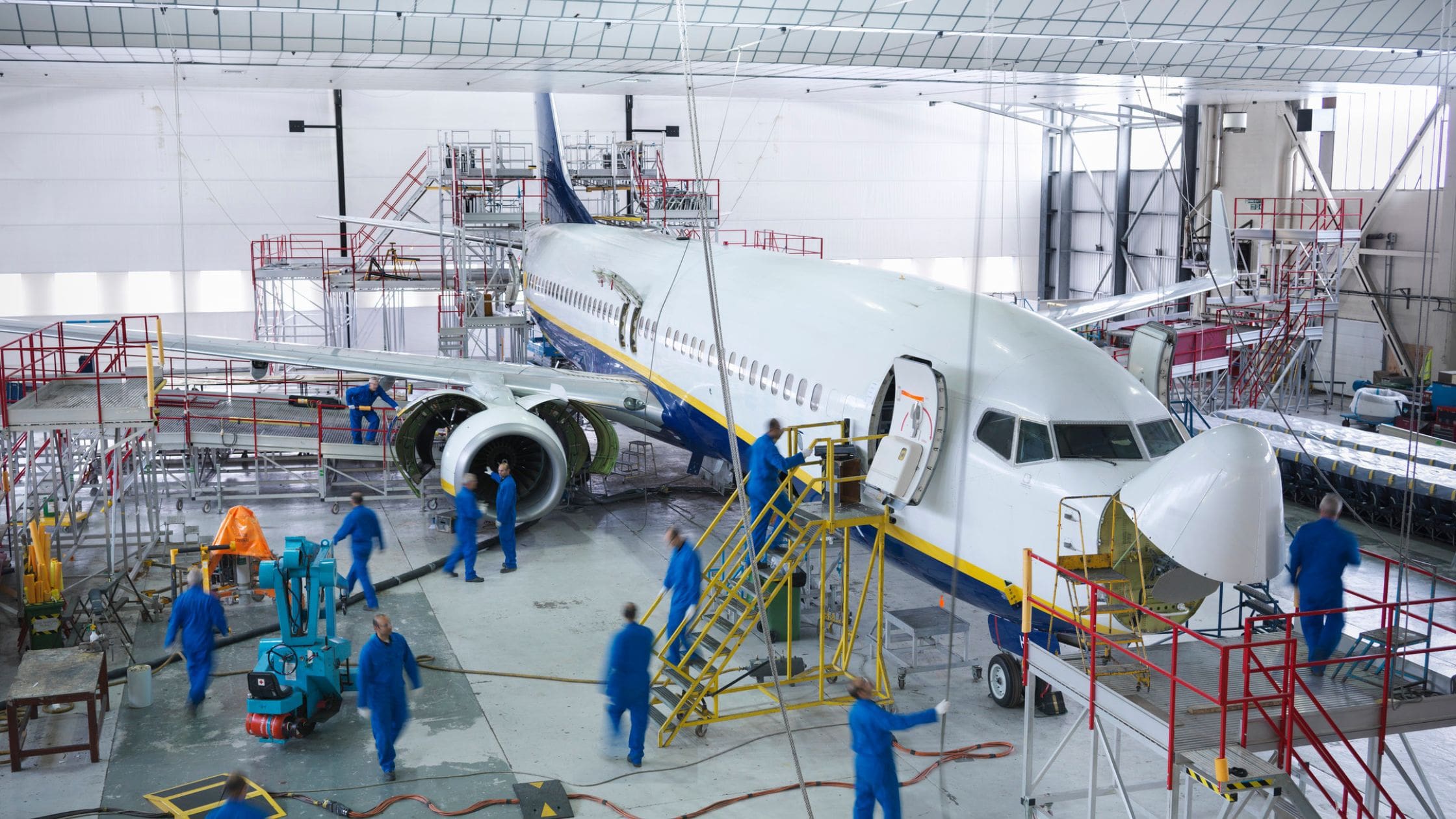

In the aerospace industry, the application of laser cutting technology is crucial. The need for lightweight, high-strength materials in this sector cannot be overstated. Precision is the hallmark of aerospace components, and laser cutting, with its high precision and ability to handle a wide range of materials, is perfectly suited for this task.
- Key aspects:
- Cutting and engraving of metals and alloys used in aircraft construction.
- Fabrication of complex components requiring meticulous accuracy.
The aerospace industry benefits from laser cutting’s ability to produce components that meet strict tolerance levels. The process, often involving fiber laser cutting or CO2 lasers, ensures that the structural integrity of materials is maintained, which is paramount in aerospace applications.
Construction Industry
Laser cutting has also made a significant impact in the construction industry. Its use in fabricating steel frameworks and detailed architectural elements has brought a new level of creativity and precision to the field.
- Examples in modern architecture:
- Laser-cut steel panels used in innovative building designs.
- Custom architectural elements that showcase intricate patterns and shapes.
The technology’s ability to cut through thick steel plates and produce precise cuts makes it an invaluable tool in construction. Whether it’s stainless steel for structural support or decorative elements, laser cutting provides a combination of strength and aesthetic appeal that is highly sought after in modern architecture.
Medical Device Industry
In the realm of medical device manufacturing, the precision and versatility of laser cutting technology are indispensable. This process, often employing fiber lasers and CO2 laser systems, allows for the creation of surgical instruments and medical implants with exceptional accuracy. The critical nature of these devices demands not only high precision but also the use of materials that are sterilizable and biocompatible.
- Key Aspects:
- The fabrication of surgical tools with intricate designs, where every millimeter can impact a patient’s outcome.
- Production of implants like stents and joint replacements, where the laser’s precision ensures the compatibility and functionality of these life-altering devices.
Laser cutting in the medical device industry is not just about creating instruments; it’s about enhancing the quality of life. The technology’s precision ensures that the tools and implants produced meet the highest standards of safety and efficacy.
Electronics Industry
Laser cutting technology plays a pivotal role in the electronics industry, especially in the miniaturization of electronic devices. The industry, constantly pushing the boundaries of how small yet efficient devices can be, relies heavily on the precision cutting capabilities of laser technology.
- Involvement in Electronics:
- Cutting intricate components for electronics and printed circuit boards (PCBs), where precision is paramount.
- Laser engraving and cutting of silicon wafers, a crucial step in semiconductor manufacturing.
This process, often involving fiber laser cutters and solid-state lasers, allows for precise control over the dimensions and quality of the cut, crucial in an industry where a fraction of a millimeter can make a significant difference.
Jewelry Industry
In the world of jewelry making, laser cutting technology has opened new doors for creativity and precision. This technology allows artisans to craft detailed designs and custom pieces that were once impossible or extremely time-consuming to make.
- Applications in Jewelry Making:
- Crafting intricate patterns in precious metals like gold, silver, and platinum.
- Customizing jewelry pieces with laser engraving, adding a personal touch to each creation.
The precision of laser cutting transforms a simple piece of metal into a work of art, showcasing the blend of technology and creativity in modern jewelry design.
Textile and Fashion Industry
The impact of laser cutting on the textile and fashion industry is profound. This technology has enabled designers to experiment with intricate patterns and designs, pushing the boundaries of fashion and textile production.
- Influence on Fashion Design:
- Cutting complex patterns in various fabrics, from delicate silks to sturdy denims.
- Enabling designers to create innovative, laser-cut garments that combine traditional materials with contemporary aesthetics.
Laser cutting in textiles not only enhances the visual appeal of the fabric but also adds a new dimension to fashion design, offering a blend of precision and artistry.
Shipbuilding and Marine Industry
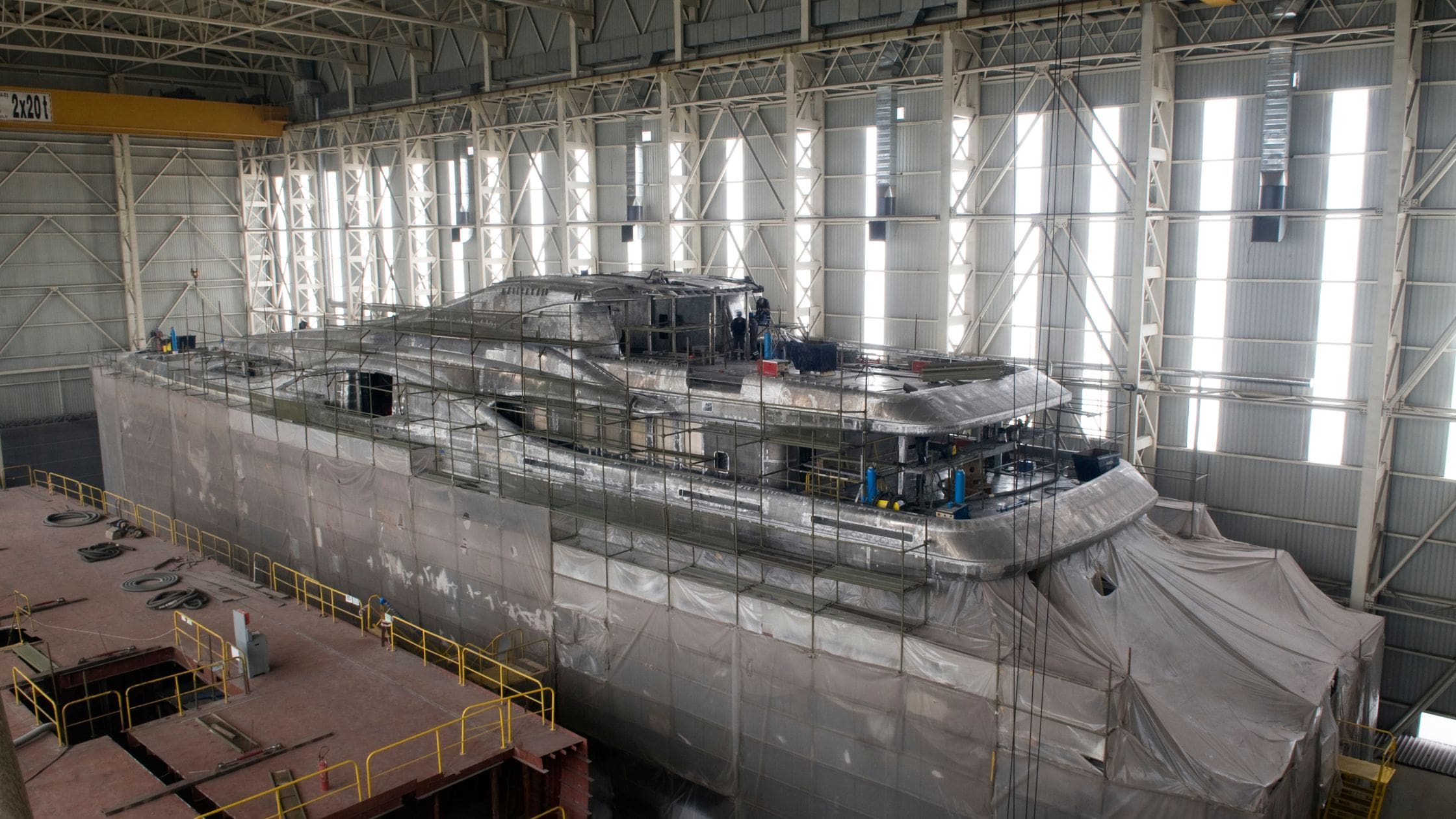

In the shipbuilding and marine industry, laser cutting technology stands as a beacon of innovation, revolutionizing the way large-scale metal parts and intricate components are crafted. The durability and precision requirements in marine applications are stringent, given the harsh marine environments these components must endure.
- Key Aspects:
- Laser cutting is used to create robust and precise components essential for shipbuilding, such as hull sections and intricate fittings.
- The technology excels in handling thick stainless steel plates, a common material in this industry, ensuring high-quality cuts and minimal waste.
The precision of laser cutting, particularly with fiber lasers and CO2 laser machines, is paramount in ensuring that each component can withstand the rigors of marine life. This precision, coupled with the technology’s ability to handle a variety of metals, makes it an invaluable tool in the marine industry.
Energy Sector (Including Renewable Energy)
Laser cutting technology plays a pivotal role in the energy sector, especially in the realm of renewable energy. The production of components for wind turbines, solar panels, and other energy infrastructure is a testament to the technology’s contribution to sustainable energy solutions.
- Contributions to Renewable Energy:
- The precision and efficiency of laser cutting are crucial in producing intricate parts for wind turbines and solar panels.
- Laser technology facilitates the creation of components with exact tolerances, essential for maximizing the efficiency of renewable energy systems.
In this sector, the versatility and high precision of laser cutting, often involving high power laser systems, underscore its importance in developing solutions that are not only sustainable but also reliable.
Machinery and Heavy Equipment Manufacturing
Laser cutting technology is heavily integrated in the manufacturing of machinery and heavy equipment. Its versatility in handling various material thicknesses and types is crucial for creating components that meet the diverse needs of this industry.
- Versatility in Manufacturing:
- From cutting thick steel plates for heavy machinery to precise components for specialized equipment, laser cutting covers a wide range of manufacturing needs.
- The technology’s ability to adapt to different materials and thicknesses without compromising precision or quality is a key advantage.
This adaptability, particularly notable in fiber laser cutting machines, ensures that manufacturers can meet the specific requirements of their projects, whether they involve heavy-duty steel or lighter metals.
Packaging Industry
In the packaging industry, laser cutting technology has become an essential tool for precision cutting of packaging materials, including the creation of intricate designs and prototypes. The customization capabilities of laser cutting are particularly valuable in this sector.
- Customization in Packaging Design:
- Laser cutting allows for the creation of unique packaging designs, including intricate cut-outs and engravings.
- The technology’s precision is ideal for producing prototypes and small batches, allowing for rapid testing and development of packaging concepts.
The ability of laser cutting to work with a range of materials, from cardboard to plastics, coupled with its precision and efficiency, makes it a favored choice in the packaging industry, where customization and quality are paramount.
Art and Sculpture
In the domain of art and sculpture, laser cutting technology has emerged as a transformative force, redefining the boundaries of artistic expression. This technology, known for its precision and versatility, allows artists to craft intricate art pieces and sculptures, previously unattainable through traditional methods.
- Impact on Artistic Expression:
- Artists harness the precision of laser cutting to create complex, detailed artworks in a variety of materials, from metals to acrylics.
- Laser cutting has enabled the creation of three-dimensional sculptures with intricate designs, adding depth and complexity to the art.
The adoption of laser technology in art and sculpture not only expands the creative possibilities but also allows for the exploration of new mediums and techniques, pushing the envelope of what is considered possible in the art world.
Furniture and Interior Design

In furniture and interior design, laser cutting technology is celebrated for its customization and design flexibility. This technology has revolutionized the way detailed wooden components, metal fittings, and decorative elements are created, offering unparalleled precision and intricacy.
- Customization in Design:
- Laser cutting facilitates the creation of bespoke furniture pieces and interior design elements, tailored to specific aesthetic and functional requirements.
- The technology allows for the precise cutting of intricate patterns and designs in a range of materials, from wood to metal, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of interior spaces.
Laser cutting’s role in furniture and interior design underscores its capacity to blend functionality with artistic expression, transforming ordinary spaces into bespoke environments.
Woodworking Industry
In the woodworking industry, laser cutting technology has become an invaluable tool. Its ability to precisely cut and engrave wood has opened up new possibilities for both functional and decorative woodworking projects.
- Applications in Woodworking:
- From intricate inlays and detailed cut-outs to precise engravings, laser cutting offers a level of detail and precision that traditional woodworking tools cannot match.
- The technology is used for creating custom furniture, decorative panels, and unique wood artworks, showcasing the material’s natural beauty in conjunction with sophisticated designs.
Laser cutting in woodworking not only enhances the quality of the final products but also significantly reduces the time and effort required in traditional woodworking methods, marking a significant advancement in the field.
Signage and Advertising
In the realm of signage and advertising, laser cutting technology stands out for its ability to produce signs, displays, and promotional materials that are both intricate and eye-catching. This technology offers a unique combination of precision, speed, and versatility, making it ideal for creating impactful marketing materials.
- Advantages in Signage and Advertising:
- Laser cutting enables the production of highly detailed and visually appealing signs and displays in a variety of materials, from acrylics to metals.
- The technology’s precision allows for the creation of complex designs that draw attention and communicate messages effectively.
The use of laser cutting in signage and advertising not only enhances brand visibility but also allows for greater creativity in design, providing businesses with a powerful tool to stand out in a crowded market.
Defense and Military
The defense and military sectors strongly benefit from the precision and reliability of laser-cutting technology. This technology is extensively used to manufacture critical parts for military vehicles, advanced weaponry, and protective gear. The high-stakes nature of defense applications demands not only precision but also consistency and dependability in every component produced.
- Key Applications in Defense:
- Fabrication of vehicle components that require high tolerance levels and strength.
- Production of intricate parts for weaponry, where every millimeter can be the difference between success and failure.
Laser cutting, with its precision cutting capabilities and ability to work with a variety of materials, including robust metals and alloys, is essential in meeting the stringent standards of the military industry.
Rail and Transportation

In the rail and transportation industry, laser cutting technology plays a crucial role in fabricating components for trains, trams, and related infrastructure. The durability and precision required in transportation applications make laser cutting an ideal choice.
- Importance in Transportation:
- Production of high-strength, precision-engineered components for rail vehicles.
- Creation of intricate parts for transportation infrastructure, where both durability and precision are critical.
The use of advanced laser cutting machines, capable of handling various material thicknesses and types, ensures the reliability and safety of transportation systems.
Agricultural Machinery Manufacturing
Laser cutting technology significantly contributes to the agricultural machinery manufacturing sector. It enhances the efficiency and durability of equipment such as tractors, harvesters, and other agricultural machines.
- Role in Agricultural Machinery:
- Precision cutting of parts for tractors and harvesters, improving the machinery’s efficiency and longevity.
- Shaping durable components that can withstand the rigors of agricultural work.
The ability of laser cutting to produce precise and durable parts is crucial in an industry where machinery is subject to harsh working conditions and demands high reliability.
Food and Beverage Industry
In the food and beverage industry, laser cutting technology is instrumental in creating machinery parts and packaging solutions. The precision required in the food processing industry, coupled with food safety considerations, makes laser cutting an invaluable tool.
- Applications in Food and Beverage:
- Manufacturing parts for food processing machinery with high precision, ensuring the safety and quality of food products.
- Producing innovative packaging solutions that meet strict hygiene standards.
The versatility of laser cutting, able to work with a range of materials, from stainless steel to food-safe plastics, plays a significant role in maintaining the high standards of the food and beverage industry.
Plastic and Polymer Cutting
The precision cutting capabilities of laser technology have revolutionized the production of complex plastic and polymer shapes and products. This industry requires a method that can intricately shape materials without compromising their integrity, and laser cutting perfectly fits this requirement.
- Innovations in Plastic and Polymer Manufacturing:
- Laser cutting allows for the creation of precise, intricate shapes in various plastics and polymers, essential for components in numerous applications.
- It offers a clean, efficient process for cutting thermoplastics, acrylics, and other polymers, which are widely used in industries ranging from automotive to consumer goods.
The non-contact nature of laser cutting means there is minimal thermal distortion, making it ideal for the delicate nature of plastics and polymers. This aspect is crucial in maintaining the quality and functionality of the final product.
Glass Cutting

Laser cutting stands out for its precision and non-contact nature, crucial for handling fragile materials like glass. This technology is widely used in both architectural and automotive applications, where precision is as important as the aesthetic quality of the cut.
- Applications in Glass Cutting:
- Precise cutting and etching of glass for architectural applications, allowing for the creation of intricate designs and patterns.
- In the automotive industry, laser cutting is used for shaping glass components, ensuring exact fit and finish.
Laser technology’s ability to make precise cuts without physical contact is a game-changer for the glass industry, reducing the risk of material breakage and enabling more complex designs.
Research and Development (R&D)
In the field of Research and Development (R&D), laser cutting technology is an invaluable tool for prototype development and experimental part fabrication. Its precision and versatility allow for the creation of components with intricate designs and tight tolerances, essential in the R&D process.
- Significance in R&D:
- Rapid prototyping of parts for testing and development, accelerating the innovation process.
- Versatile in handling a variety of materials, which is crucial for experimental projects that may require working with unique or composite materials.
Laser cutting’s ability to quickly and accurately produce parts plays a critical role in the iterative process of R&D, driving forward the development of new technologies and products.
Sports Equipment Manufacturing
In sports equipment manufacturing, laser cutting technology is used to produce components that are not only functional but also customizable. The industry requires materials that vary greatly in terms of type and thickness, and laser cutting’s versatility makes it a perfect fit.
- Enhancements in Sports Equipment Design:
- Customization of sports gear and equipment, tailored to specific athletic needs and preferences.
- Ability to work with a variety of materials, from metals for structural components to plastics and composites for specialized gear.
The precision and material versatility of laser cutting are essential in sports equipment design, where performance and safety are paramount. This technology allows for the creation of equipment that enhances athletic performance and provides better protection.
Tool and Die Industry
In the tool and die industry, laser cutting technology has become indispensable, especially for cutting and shaping tools, dies, and molds. This industry demands not just precision but also the ability to handle materials of varying hardness, and laser cutting rises to this challenge effectively.
- Precision and Material Hardness Capabilities:
- The laser cutting process is adept at shaping hard materials used in tool and die making, maintaining precision even with tough metals.
- It allows for the creation of intricate shapes and patterns in dies and molds, which are essential for manufacturing various products.
The precision of laser cutting ensures that each tool and die component is made to exact specifications, which is crucial for the high-quality production of goods in various industries.
Rubber and Gaskets Industry
In the rubber and gaskets industry, laser cutting plays a critical role in producing precision gaskets and seals. The clean cuts and consistency provided by laser technology are crucial in applications where perfect sealing is a necessity.
- Importance in Sealing Applications:
- Laser cutting allows for exact dimensions and shapes in gaskets and seals, ensuring a perfect fit and preventing leaks.
- The technology’s ability to produce clean, precise cuts is essential for the integrity of seals used in various industries, from automotive to aerospace.
The non-contact nature of laser cutting means there is minimal risk of deforming the rubber or gasket materials, further enhancing the quality of the final product.
Education and Academia
In education and academia, laser-cutting technology is widely used in educational workshops and engineering projects. Its role in prototyping and educational models is significant, as it allows students and researchers to bring their ideas to life with precision and ease.
- Role in Prototyping and Educational Models:
- Laser cutting is utilized in educational settings for creating detailed models and prototypes, aiding in the learning process.
- The technology provides students with hands-on experience in manufacturing and design, preparing them for future careers in various fields.
The precision and versatility of laser cutting make it an ideal tool for educational purposes, encouraging innovation and practical learning in academic settings.
Event and Stage Design
In event and stage design, laser cutting technology is employed to produce intricate designs for stages, events, and exhibitions. The technology offers creative possibilities and quick turnaround times, which are essential in the fast-paced world of event planning.
- Creative Possibilities in Event and Stage Design:
- Laser cutting allows for the creation of elaborate and unique designs for stage sets and event decorations, enhancing the visual appeal.
- The technology’s ability to work quickly and precisely is crucial in meeting the tight deadlines often associated with event and stage production.
The flexibility and efficiency of laser cutting make it a valuable tool for designers and artists in the event and stage design industry, where creativity and timely execution are key.
What Materials Can Be Effectively Cut Using Lasers?

As versatile as it is, it is no wonder that laser-cutting technology allows for intricate cutting of a wide variety of materials.
Here, we explore the materials that are most effectively cut using lasers, each chosen for their unique properties and the specific advantages they offer in laser processing.
- Stainless Steel: A popular choice for its strength and resistance to corrosion, ideal for both industrial applications and consumer products.
- Mild Steel: Known for its malleability and effectiveness in construction and automotive industries.
- Aluminum: Lightweight yet strong, used extensively in aerospace and transportation sectors.
- Titanium: Valued in aerospace and medical industries for its strength and biocompatibility.
- Copper: Used in electrical components due to its excellent conductivity.
- Brass: A combination of copper and zinc, often used in decorative applications for its golden appearance.
- Acrylic: Widely used in signage and displays for its clarity and ability to be laser cut with clean, polished edges.
- Wood: From hardwoods to plywoods, laser cutting provides intricate detailing for furniture, art, and more.
- Glass: Precision and non-contact nature of laser cutting make it suitable for delicate glass cutting, particularly in architectural and automotive applications.
- Plastics and Polymers: Includes a variety of types, each offering different characteristics suitable for laser cutting, like PETG, ABS, and polycarbonate.
The choice of laser – be it a CO2 laser, fiber laser, or solid-state laser – depends on the material being cut.
Factors like thickness, heat sensitivity, and desired precision play a crucial role in determining the suitable type of laser and cutting process.
Conclusion
The exploration of laser cutting technology in various industries reveals its remarkable versatility and efficiency. From intricate designs in the art and fashion world to precision components in aerospace and automotive industries, the applications of laser cutting are vast and diverse.
Its ability to work with a wide range of materials – metals, plastics, glass, and more – underscores its adaptability and indispensability in modern manufacturing.
As we look towards the future, the potential for laser cutting technology only expands.
Advancements in laser power, efficiency, and control will likely open new avenues in material processing and design capabilities, further expanding the laser cutting application area. The ongoing integration of laser cutting with other technological innovations, such as 3D printing and advanced CNC techniques, suggests a future where the boundaries of manufacturing and creativity are continually pushed forward.
For you, whether you’re a manufacturer, designer, engineer, or hobbyist, understanding the capabilities and applications of laser cutting is more than a technical necessity; it’s a gateway to innovation and precision in whatever you create.
As laser technology continues to evolve, it promises to remain a vital tool in shaping the world around us, from the objects we use every day to the most advanced technologies.







